Where there is a Will, there is a Way
"We see here a towering cliff belonging to a mountainous range which rises like a wall, or barrier,…

Climb Not Too High, Lest the Fall be Greater
"While treading on our course this earthly ball, / We often stumble, and we sometimes fall: / 'Get above…

The Great Sphinx
"This colossal figure, human-headed and lion-bodied, is hewn from the natural rock. The body is about…

The Mound at Marathon
"Near the southern extremity of the plain of Marathon rises a conical mound, 30 feet high. it covers…

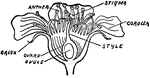
Group of Gods and Goddesses
"The chief gods, in striking contrast with the monstrous divinities of the Oriental mythologies, had…

Prow of a Roman War Ship
"The representation shows the arrangement of the tiers or oars in a two-banked ship. In just what way…
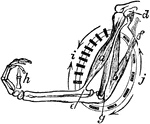
Muscular Cycle of the Biceps
A diagram showing the muscular cycle form by the biceps or flexor muscle, and the triceps or extensor…
Wing of Bird
"Shows how the bones of the arm (a), forearm (b), and hand (c), are twisted, and form a conical screw."—Pettigrew,…
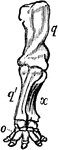
Anterior Extremity of Elephant
"Shows how the bones of the arm (q), forearm (q'x), and foot (o), are twisted to form an osseous screw."—Pettigrew,…
Heart of a Deer
"Cast or mold of the interior of the left ventricle of the heart of a deer. Shows that the left ventricular…

Compressed Foot
An extreme form of a compressed foot, typically seen in the deer and ox. It is useful for land transit.

Foot of Seal
"Foot of the seal, which opens and closes in the act of natation, the organ being folded upon itself…

Red-Throated Dragon
"The Red-Throated Dragon shows a large membranous expansion (b b) situated between the anterior (d d)…
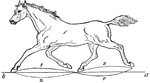
Trotting Horse
"Horse in the act of trotting. In this, as in all the other paces, the body of the horse is levered…
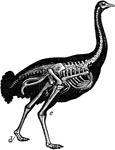
Skeleton of Ostrich
"Shows the powerful legs, small feet, and rudimentary wings of the bird; the obliquity at which the…
Overhand Swimming
"The overhead movement enables the swimmer to throw himself forward on the water, and to move his arms…
Side-Stroke Swimming
"An improvement on the foregoing for long distances is the known as the side stroke. In this method,…

Large Beetle
"Under surface of large beetle, with deeply concave and comparatively small wings, shows that the nervures…
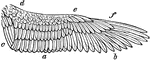
Right Wing of Kestrel
"Right wing of the Kestrel, drawn from the specimen, while being held against the light."—Pettigrew,…

Northern Lapwing
"The Lapwing with one wing fully extended, and forming a long lever; the other being in a flexed condition…

Dragonfly
An insect characterized by large multifaceted eyes, two pairs of strong transparent wings, and an elongated…

The Pigeon
"The Pigeon flying downwards and turning prior to alighting. The pigeon expands its tail both in ascending…

Winged Bull
An ancient Assyrian wall relief, depicting the symbol of a winged bull with the head of a human male.
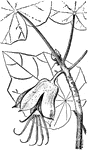
Hand Flower
Hand flower is the common name of chiranthodendron platanoides. The bright red stamens resemble the…
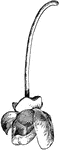
Cymbopetalum Penduliflorum
The flowers of cymbopetalum penduliflorum grow alone at the end of each stem. The petals and thick and…
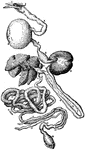
Fowl Digestion
The digestive system of a fowl. 1 is the tongue, 3 is the crop, 6 is the gizzard, 10 is the small intestine,…
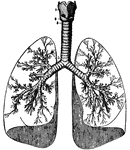
Human Lungs
Human lungs. 1 and 2 make up the larynx, or voice box. 1 is thyroid cartilage, 2 is cricoid cartilage.…
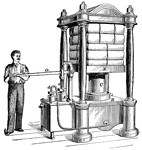
Hydraulic Press
A hydraulic press which uses a hydraulic cylinder to generate force. The inventor of the device, Joseph…
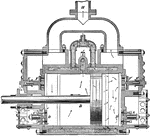
Air Compressor
An air compressor. They come in many forms, most commonly in cylinder form - as shown. This image shows…
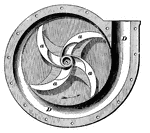
Centrifugal Pump
This image is a centrifugal pump with one half of the casing removed. S is a hollow hub, a is a curved…
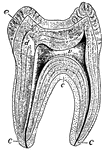
Human Tooth
A sectional view of a human molar. The roots, or fangs, are shown covered by a layer of bone called…
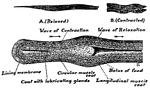
Human Esophagus
An Image of an esophagus showing how a mass of food, or bolus, passes through the esophagus into the…
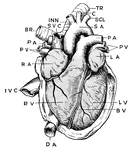
Anatomy of Heart
A complex anatomical view of the heart. RA is the right atrium, or auricle, which receives the deoxygenated…
Striated Muscle
Striped, or striated, muscle which quickly contracts causing the alternating black and white lines.…
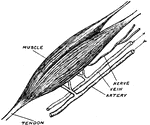
Bicep Muscle
The upper bicep of the right arm. Included are the tendons, blood vessels, and its nerve.
Nerve Cell
A simple nerve cell, or neuron. N is the nucleus of the cell, NC is the cytoplasm, D are dendrites which…
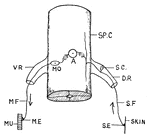
Reflex Action
Illustration of the reflex action of an animal. SE is the sensory nerve-ending. A stimulus passes through…
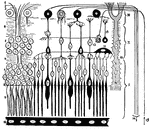
Eye Retina
Diagram of the retina, aka percipient layer of the eye. 1: inner limiting membrane, which is next to…
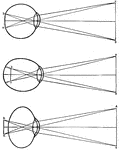
Human Eye
Diagrams of how an image is displayed with a normal eye (top image), myopic or nearsighted eye (middle…
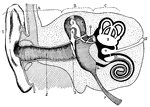
Human Ear
A diagram of the human ear. It is divided into the outer ear - A, middle ear - B, and inner ear - C.…
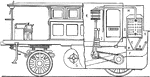
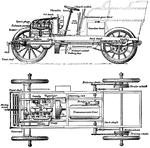
Hancock Coaches
A Hancock Coach cross-sectioned in order to display the engine and driving connections. (A) is the exhaust…
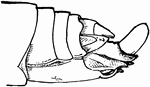
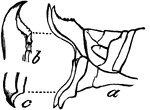
Locust Anatomy
Enlarged end of the female, showing oviposition: the oviduct, the egg guide, and the egg issuing from…
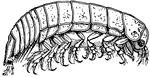
Limnoria Lignorum (Flabellifera)
Flabellifera are a tribe of isopods. Their bodies end in a tail fan, made by the last pair of appendages…
Nerve Ganglia (Spinal)
Nerve Ganglia, or Knots (sing. Ganglion; Knot) occur as collections of nerve cells on the course of…

Clermont Gargoyle
This illustration shows a Clermont Gargoyle in France. Gargoyles, in Gothic architecture, are spouts…